Bitten in a Fight - What Happens Next?
What happens when you get bit during a confrontation
Author: Garland H. - (Silat Sharaf Practitioner, ER Nurse)
Mike Tyson bites Evander Holyfields’ ear in a match
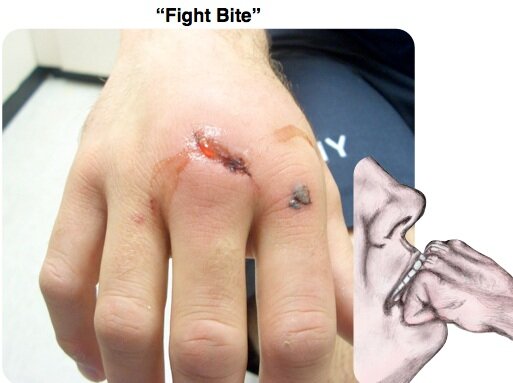
Human Bites and Clenched Fist Injuries
· Note…I’m not an MD. These are for entertainment purposes only. I don’t want anyone suing me or being sued for practicing medicine. 😊
According to UpToDate (2020), there are approximately 250,000 human bites each year in the United States alone. Of those, a quarter will become infected. The likelihood of infection varies on the depth and location of the wounds. Superficial wounds may only have a 2% likelihood of becoming infected, whereas clenched fist injuries hover around 25%.
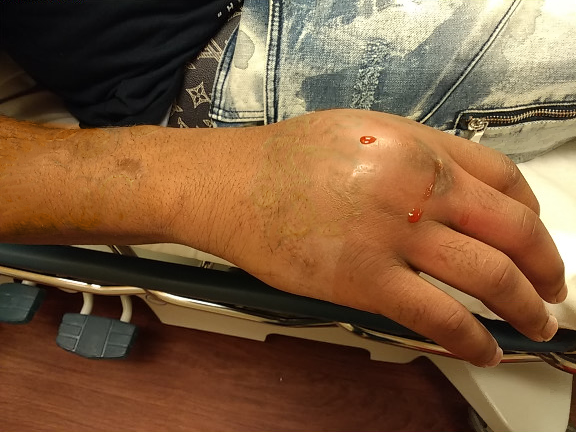
A clenched fist injury
Human bites sometimes occur in the context of domestic violence and sexual assault. Health care workers who work in with particular populations are also at risk of being bitten. Naturally, they can also occur during a fight, especially when an individual feels like they are losing and in an otherwise unrecoverable position. Clenched fist injuries happen when a bare fist meets exposed teeth. Usually, this occurs on the knuckles, and these are especially prone to infection. Note: striking somebody with a palm doesn’t prevent a fight bite, it just changes the potential area being sliced open. I’ve seen somebody fillet the inside of their palm and wrist on teeth.
Human bites are no joke. While I was working in inpatient psych, I was bitten by a patient in my upper arm and axillary area. Although the skin was only broken in a few places, I still presented to the emergency room and was given tetanus shots and put on post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) in case the person had HIV and a battery of antibiotics. I had to do follow up visits for serial Hep B and Hep C tests to make sure I wasn’t exposed.
Sepsis steps
Infected bites can cause septicemia. Sepsis is one of the leading causes of death in hospital settings. Early treatment with antibiotics is of paramount importance. Every human bite should be seen by a medical professional and treated as an emergency.
“Vegetation” on heart valve
Besides sepsis, cellulitis, osteomyelitis, and septic arthritis, one of the germs found in the human mouth, Eikenella corrodens, has the potential to cause culture-negative endocarditis, wherein “vegetation” (bacteria surrounded by a layer of platelets and fibrin) can form on the heart valves causing a potentially life-threatening situation which may require heart surgery.
Other common organisms found in human bites are Viridians streptococci, Staphylococcus epidermis, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacteroides sp., Corynebacterium, & Peprostrptococci. Antibiotic therapies are usually 3-5 days for prophylaxis, whereas superficial infections run up to 14 days, longer if there are additional complications. Deep infections require IV antibiotics and hospitalization.
Among the effects of a human bite
External accoustic meatus bitten through
Swollen
Fight-bite effect
compartment syndrome secondary to fight bite
Treatment
Irrigation of the wound with sterile water or normal saline will help remove debris and wash out the injury. If there is a suspicion that the person who bit you has HIV, hepatitis, or other viral infections, wash the wound with a virucidal agent like povidone-iodine. A good way to provide enough pressure while irrigating is to use a large syringe (50 or 30cc) with a large IV angiocath (just the plastic, 18, 16, and 14 gauges are all acceptable) as a means of spraying the liquid into the wound bed. It hurts like hell, so if you are trained to do it and have access to the requisite supplies, a local nerve block by infiltrating lidocaine (not with epi in the hands) is probably a conscientious thing to do.
Wound irrigation procedure
Wound closure may be accomplished by suturing or dermabond (medical superglue) depending on the nature (jagged or approximated edged) and depth of the wound. If the wound is 12-24 hours old when the individual is seeking treatment, leave the wound open.
Applying dermabond
If tendons are affected in the hands- a hand surgeon would be a good thing to get a referral for. If it is a disfiguring injury, plastics should be consulted.
Antibiotics: to be determined by the medical provider.
Keep the wound clean and dry, following your post-visit medical instructions, and expect the doctor to schedule a follow-up appointment for 1 to 2 days out.
PEP: post-exposure prophylaxis for viral infections. To be discussed with the provider.
Elevation and Swelling Management: propping up the affected area with pillows, take Tylenol for the swelling (read the instructions carefully, Tylenol/APAP/paracetamol is not as benign as you may imagine, don’t overdo it), and an ice pack is all good ideas.
Biting is a common tactic but getting bit is never a fun experience. Do seek professional medical aid instantly after being bitten or wounded. More often than not it can save your life.